Which Best Describes the Regulation of Thyroid Hormones
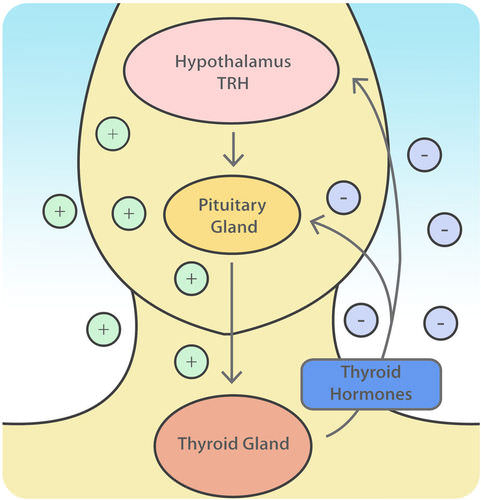
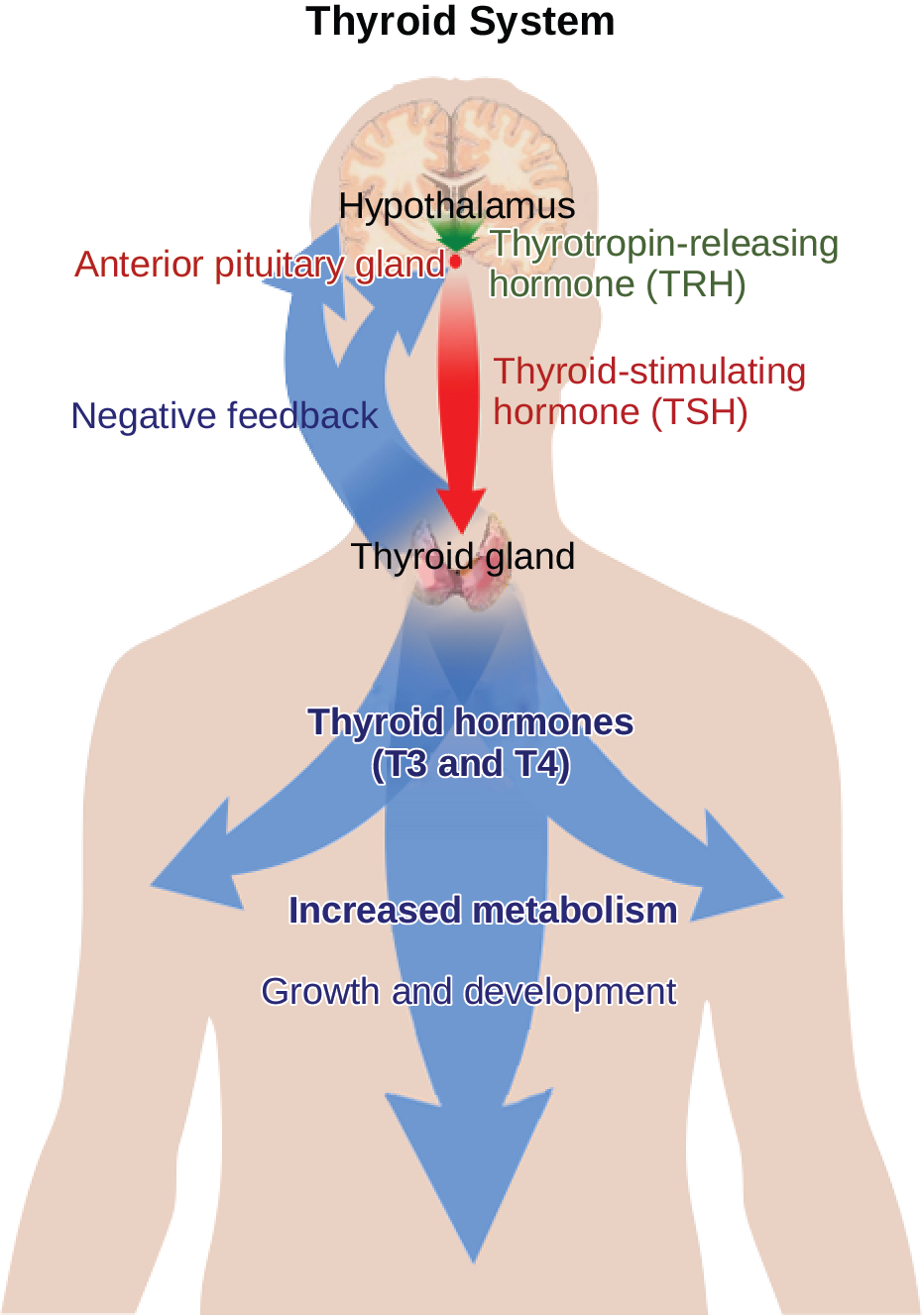
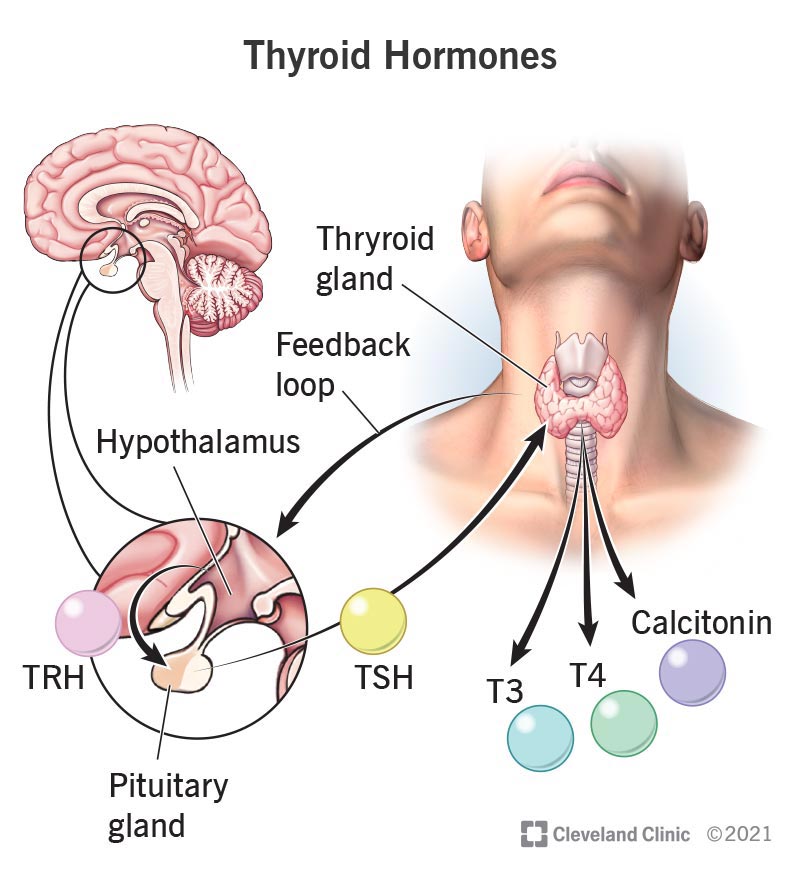
TRH stimulates the pituitary gland to produce thyroid-stimulating hormone or TSH. T4 and T3 are hormones produced by the thyroid gland and are essential for life.
Hormone Regulation Ck 12 Foundation
T3 is the active form of thyroid hormone in that it influences many body processes in particular the regulation of metabolism 1 2Summary.
. A They include direct and tropic hormones. Thyroid Hormone Regulation Overview Thyroid Hormone release is regulated by an extended version of the circuit that governs Basic Hypothalamic-Pituitary. Which of the following is involved in the regulation of thyroid hormone levels.
The thyroid gland is regulated by thyrotropin releasing hormone TRH and thyroid stimulating hormone TSH. A classic negative feedback loop controls the regulation of thyroid hormone levels. All of the following are true of posterior pituitary pituitary hormones EXCEPT.
The anterior pituitary releases the thyroid-stimulating hormone which then stimulates the thyroid gland to produce the hormones T 3 and T 4. B They are released from the posterior pituitary. The anterior pituitary releases the thyroid-stimulating hormone which then stimulates the thyroid gland to produce the hormones T 3 and T 4.
The production and secretion of thyroxine and triiodothyronine by the thyroid gland are stimulated by the hypothalamic hormone thyrotropin-releasing hormone and the anterior. As at any factory effective production depends on three key components - adequate raw material efficient machinery and appropriate controls. TRH stimulates thyrotropin cells in the anterior pituitary to the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone TSH.
To maintain their availability there are large stores of thyroid hormone in the circulation and in the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is one component of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis which is a prime example of a negative feedback control system. Regulation of thyroid hormone secretion.
The hypothalamic-pituitary axis regulates TSH release. Regulation of Thyroid Hormone. It has two lobes connected by a central portion called the commissure.
It is brought about by the negative feedback mechanism. Iodide exits this pool from the blood into the follicular cells of the thyroid gland Mechanism for iodide transport into. The loop includes the hypothalamus and pituitary gland in addition to the thyroid.
Heres how thyroid regulation works. The hypothalamus releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone TRH into the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system to the anterior pituitary gland. What are the Thyroid hormones.
The thyroid hormones are secreted by the thyroid gland which is located in front of the neck. 101007s00360-016-0984-2 Abstract Thyroid hormone TH regulates many physiological processes that differ between tissues developmental stages and in response to specific environmental cues. C Hormones are transported through the blood stream to target cells.
C A nerve signal from the hypothalamus stimulates their release. E Hormones travel through the lymphatic system to target cells. Functions of Thyroid Hormones The thyroid hormones T 3 and T 4 are often referred to as metabolic hormones because their levels influence the bodys basal metabolic rate the amount of energy used by the body at rest.
A Hormones are released at synapses adjacent to target cells. It is the primary stimulus for thyroid hormone production by the thyroid gland. It should be pointed.
The most important factors are as follows. Thyroid-stimulating hormone also known as TSH is a glycoprotein hormone produced by the anterior pituitary. It secretes thyroid hormone in response to stimulation by TSH.
The main function of the thyroid gland is to make hormones T4 and T3 which are essential for the regulation of metabolic processes throughout the body. It can therefore play very different signaling roles depending on specific physiological contexts. Figure 1742 Classic Negative Feedback Loop.
Regulation of thyroid hormone starts at the hypothalamus. So T4 is basically a stepping stone required for T3. Regulation of thyroid hormone secretion.
It requires iodine to synthesize thyroid hormone. 9 rows The most significant pathway that interacts with TH regulation of metabolism is adrenergic. The anterior pituitary in turn releases hormones that regulate hormone production by other endocrine glands.
1 Thyroid stimulating hormone TSH. These hormones are integral in the regulation of many functions and aspects of the human body such as temperature regulation energy levels weight hair nail growth and more. Thyroid hormones must be constantly available to perform these functions.
It is located on the anterior surface of the trachea inferior to the thyroid cartilage. Regulation of Thyroid Hormone Synthesis Ingested iodine is mostly absorbed from the gut in the form of iodide to enter an extracellular iodide pool. The thyroid produces mainly T4 which is then converted to T3 in tissue and organs.
Thyroid hormones are critical determinants of brain and somatic development in infants and of metabolic activity in adults. The hypothalamus secretes thyrotropin-releasing hormone or TRH. D Ducts transport hormones directly to target cells.
The primary synthetic organ of Thyroid Hormones is the thyroid gland which produces about twenty times more T 4 compared to T 3. B Hormones are produced by endocrine cells that are adjacent to target cells. Increased proteolysis of thyroglobulin early important effect Increased activity of iodide pump.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone from the anterior pituitary Blood Ca2 levels Positive feedback mechanisms PTH parathyroid hormone levels Thyroglobulin in thyroid follicles. Increase in free form of hormone in circulation acts on hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland. Thyroid Hormones are amine hormones and so their synthesis is based on the amino acid tyrosine.
It also exerts growth effects on thyroid follicular cells leading to enlargement of the thyroid. There is involvement of hypothalamo- pituitary-thyroid axis Fig. They also affect the function of virtually every organ system.
A An action of TSH. T 4 is then converted to either T 3 or rT 3 by the enzyme Iodinase which is present throughout the bodys tissues. The hypothalamus releases Thyrotropin-releasing Hormone TRH which acts on the anterior pituitary.
The thyroid gland produces two hormones. There are several factors which help to keep the secretion rate and normal level of T 3 and T 4 in the serum. In addition to TRHTSH regulation by TH feedback there is central modulation by nutritional signals such as leptin as well as peptides regulating appetite.
The anterior pituitary in turn releases hormones that regulate hormone production by other endocrine glands. An enlargement of the thyroid gland is called a goiter. The thyroid gland is regulated by a negative feedback loop.
D They include ADH and oxytocin.
Thyroid Hormone What It Is Function

Regulation Of Hormone Production Biology 2e
18 4 Regulation Of Hormone Production Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition

Thyroid Hormone Synthesis Regulation And Mechanism Of Action Youtube

Comments
Post a Comment